SpaceTech Weekly Recap – September 29 - October 05, 2025
Major funding, new missions, and setbacks: what mattered last week in space innovation.
Each week we bring you a curated look at the biggest moves in SpaceTech – from funding and M&A to market trends, contracts, and a quick stock snapshot.
“This week highlights strong investor interest in practical, mission-critical SpaceTech: funding flowed to companies advancing rugged SATCOM, autonomous drones, additive propellants, and satellite IoT. Strategic acquisitions and international partnerships indicate the sector values scalable, reliable, end-to-end solutions with government or global backing. In line with this momentum, Rocket Lab’s stock surged to a new all-time high, reflecting growing investor confidence. This uptick follows the company’s announcement of securing its largest single-customer order for 10 additional Electron launches with Synspective, a Japanese satellite operator, further solidifying its position in the market. Activity continues a pattern of strong interest in operationally ready SpaceTech solutions.” - Commentary by Matej Pretković
We provide consulting, fundraising support, market research, and advisory to help you grow and succeed. Contact us at mpretkovic@cyclopcorp.com.
Here is a quick overview of news:
M&A & Funding
Commcrete Secures $29M to Advance Compact Tactical SATCOM
Orbotix Raises €6.5M for Autonomous Defense Drone Development in Europe
Firehawk Aerospace Closes $60M Series C to Scale Additive Rocket Propellants
Hubble Network Raises $70M Series B to Expand Satellite Bluetooth IoT
Intuitive Machines Acquires KinetX to Strengthen Deep-Space Navigation
Market
OQ Technology Expands Satellite IoT Services to Australia
Launch
Firefly Alpha Rocket Destroyed During Preflight Test
Contracts
Rocket Lab and Synspective Secure 10 More Electron Launches
Arianespace and BULL Partner on Ariane 6 Space Debris Mitigation
NASA and Australia Sign Bilateral Aeronautics and Space Cooperation Agreement
ESA and KASA Formalize Collaboration on Space Weather and Ground Station Use
Synspective Adds 10 More Electron Launches for StriX Constellation
Solstar Wins NASA SBIR Contract to Develop Lunar Wi-Fi System
Avio Secures €40M ESA Contract for Reusable Upper Stage Demonstrator
Beyond Gravity to Supply Robotic Arms for SWISSto12 GEO Satellites
Read our latest weeklies for more recent SpaceTech updates
Stay up to date with funding, deals, trends, contracts, and market insights in one weekly update.
Weekly SpaceCap - These tables track weekly stock performance and key metrics for global and European SpaceTech companies, giving a quick snapshot of market trends.
US – SpaceTech Stocks Snapshot
Europe – SpaceTech Stocks Snapshot
Need a full breakdown by sector or a customized template with your own metrics? Get in touch with us at mpretkovic@cyclopcorp.com.
Read the news in more detail:
M&A & Funding
Commcrete Secures $29M to Advance Compact Tactical SATCOM
What happened: Commcrete, an Israeli tactical SATCOM startup founded by elite defense veterans, has raised $29 million across Seed and Series A to develop handheld systems for soldiers, first responders and security agencies. The $21 million Series A was led by Greenfield Partners, with Redseed Ventures and existing backers; Amnon Shashua’s Q Fund also participated. The company, with about 40 employees in Israel and the U.S., offers Flipper, Stardust and Bittel for secure, multi-channel communication without clear sky access or heavy antennas.
Why it matters: The funding backs a move toward ultra-compact SATCOM that can function with minimal sky visibility, reducing dependence on bulky ground stations and constant transmissions. Commcrete claims its technology delivers up to ten times the performance of traditional systems, with a lighter, smaller footprint. The devices have already proven useful in a 2023 natural disaster and in international rescues and regional conflicts lacking reliable conventional links, signaling demand for rugged handheld SATCOM.
Investor angle: Commcrete’s funding supports a niche but growing demand for rugged, handheld SATCOM that operates without heavy infrastructure. Backers highlighted include Greenfield Partners and Amnon Shashua’s Q Fund, alongside Redseed Ventures, underscoring strategic interest from defence-technology veterans. The potential upside lies in expanding military, emergency, and security applications worldwide, though success will hinge on defense contracts, field reliability, and ability to scale production beyond 40 employees.
Orbotix Raises €6.5M for Autonomous Defense Drone Development in Europe
What happened: Polish startup Orbotix has secured a €6.5 million funding round to accelerate the development of autonomous defense drones across Europe. The financing supports Orbotix’s efforts to advance drone autonomy and expand its activities within the European defense technology landscape. This marks a strategic step for a Polish firm seeking to establish a foothold in Europe’s evolving autonomous weapon systems market.
Why it matters: The investment underscores continued interest in European defense technology and autonomous aerial systems, with capital directed toward domestically developed drone capabilities in Europe. It highlights a trend of funding for regional players aiming to advance autonomy and defense-grade platforms. The European market context and regulatory landscape remain factors that influence deployment timing.
Investor angle: For investors, the €6.5 million round signals confidence in Orbotix’s approach to autonomous defense drones and potential European expansion. The deal suggests appetite for defense-tech startups in the region, but investors should monitor milestones, potential partnerships with customers, and regulatory approvals that could affect value realization and time to market.
Firehawk Aerospace Closes $60M Series C to Scale Additive Rocket Propellants
What happened: Firehawk Aerospace closed an oversubscribed $60M Series C on Sep 24, 2025, led by 1789 Capital, and added Presto Tech Horizons as a strategic European investor (a fund for med by Presto Ventures and CSG). Firehawk says the capital will scale production of its 3D-printed energetics/solid rocket motors, expand facilities, and strengthen allied defense-supply-chain resilience.
Why it matters: Global demand for munitions and propellants is outpacing legacy capacity; Firehawk’s additive-manufactured propellant aims to deliver faster, safer, more flexible production—helpful for U.S.–EU co-production and replenishment needs. The raise also follows program traction (e.g., recent U.S. Army flight-test milestone on Javelin/Stinger-class motors), signaling a shift from R&D to scale.
Investor angle: The oversubscribed $60M Series C, with transatlantic strategic investors, helps fund production scale-up of its additive-manufactured propellants, which promise faster lead times, safer handling, and design flexibility—potential advantages in qualification and cost curves. Key upside catalysts include facility ramp, qualification wins, and multi-year procurement or co-production deals; principal risks center on certification timelines, concentration of defense buyers, and entrenched incumbents.
Hubble Network Raises $70M Series B to Expand Satellite Bluetooth IoT
What happened: Hubble Network announced a $70 million Series B funding round, bringing total funding to $100 million since its 2021 founding. The round was led by Ryan Swagar, with new investors including Tom Gonser, Mike Farley, Marc Weiser, Tuff Yen, and Y Combinator. The funds are said to accelerate the expansion of Hubble’s Bluetooth-to-satellite network, building on milestones such as seven operational satellites and an exclusive Life360/Tile partnership connecting into a 90 million-smartphone ecosystem.
Why it matters: The funding underscores growing investor confidence in satellite-enabled IoT connectivity powered by Bluetooth technology. Hubble’s approach leverages existing Bluetooth chips and a developer-first platform to lower costs, simplify integration, and accelerate adoption of space-based connectivity. With seven satellites in orbit and a major partnership linking millions of smartphones, the company aims to scale global coverage, support enterprise deployments in logistics, infrastructure, defense, and consumer IoT, and broaden the addressable market for satellite IoT.
Investor angle: The Series B signals validation of a long-run opportunity to build a global, low-power, ubiquitous satellite network for billions of IoT devices. The round brings strategic capital with expertise across SaaS, IoT, consumer, and space, and supports a path to expanded constellation, developer ecosystem, and enterprise deployments. Risks include space-tech capital intensity and execution, but the exclusive Life360/Tile partnership and proven milestones may help de-risk near-term adoption and monetization prospects.
Intuitive Machines Acquires KinetX to Strengthen Deep-Space Navigation
What happened:On October 1, 2025, Intuitive Machines closed its previously announced purchase of KinetX, Inc. for $30 million before closing adjustments, paid as ~$15 million in cash plus ~1.4 million LUNR shares. KinetX brings certified deep-space navigation, systems engineering, and constellation mission-design expertise. Intuitive Machines says it will combine KinetX navigation with its spacecraft and data-service platform to deliver secure communications and precision navigation for lunar and interplanetary missions.
Why it matters:The deal vertically integrates a critical function—deep-space navigation and mission planning—into Intuitive Machines’ lunar landers and upcoming data-relay services, aiming to shorten delivery timelines and offer end-to-end solutions from the Moon to Mars. KinetX’s NASA-certified track record (missions to Mercury, Pluto, asteroids, and the Moon) strengthens Intuitive Machines’ credibility for civil and national-security customers and positions it for the emerging cislunar communications/navigation market.
Investor angle: This is a classic capability tuck-in that deepens moat and shifts mix toward recurring, service-like revenue (navigation, constellation ops, data relay). Synergies include faster program execution, stickier customer relationships, and eligibility for larger, integrated contracts. Key watch-items: integration pace, conversion of pipeline into multi-year awards, and capital discipline as the company scales beyond lunar missions.
Market
OQ Technology Expands Satellite IoT Services to Australia
What happened: OQ Technology announced that it is expanding its satellite-based Internet of Things (IoT) services to Australia, signaling the company’s intent to broaden its geographic coverage. The article’s content centers on this expansion; no further details, timelines, or product specifications are provided in the text.
Why it matters: The expansion indicates OQ Technology is broadening its global footprint for satellite IoT services, potentially aligning with growing demand for remote connectivity and machine-to-machine communications in new markets. It highlights ongoing industry trends toward satellite-based IoT and geographic diversification for providers, though no financial metrics or implementation details are disclosed.
Investor angle: The expansion could broaden revenue opportunities and diversify geographic risk for OQ Technology. However, the article does not provide financial data, timelines, or customer information, so readers should await further details on go-to-market plans, pricing, and expected impact on valuation before making investment decisions.
Lunch
Firefly Alpha Rocket Destroyed During Preflight Test
What happened: Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha rocket exploded during a preflight test, according to Space. The incident occurred before liftoff while preparing for a test flight. The article provides no details on the cause of the explosion, whether there were any injuries, or the next steps for the Alpha program; it notes only that the event happened during preflight testing.
Why it matters: While the article does not discuss causes or consequences, the explosion highlights the risks inherent in testing new launch vehicles in the private spaceflight sector. Such preflight-test failures can affect program timelines, trigger safety reviews, and influence stakeholder confidence in developers’ ability to advance complex propulsion projects. In the broader industry, such incidents can shape expectations for pace, cost, and reliability of private launch programs.
Investor angle: The explosion introduces risk to Firefly’s Alpha program and could affect perceptions of development timelines and reliability. The article does not mention financial implications or funding, but a significant test failure can raise questions about milestone delivery and future capital needs, potentially influencing valuations and financing decisions for Firefly Aerospace.
Moon Mission Maker Firefly Aerospace Launches IPO on the Nasdaq
Firefly Aerospace has launched its IPO today, trading under the ticker symbol FLY on the Nasdaq exchange.
Contracts
Rocket Lab and Synspective Secure 10 More Electron Launches
What happened: Rocket Lab, the U.S.-based launch services provider, has signed a second multi-launch deal with Japan’s SAR satellite company Synspective for 10 additional dedicated Electron launches. This brings the total number of upcoming Synspective missions to 21, making it Rocket Lab’s largest single-customer Electron order to date. Rocket Lab has previously launched six StriX SAR satellites for Synspective from its New Zealand site, with all future launches also planned from there.
Why it matters: The contract highlights Electron’s reliability, schedule flexibility, and precision, reinforcing Rocket Lab’s leadership in the small-lift launch market. Synspective’s growing constellation of 21 StriX satellites will enhance its SAR data platform, supporting Earth observation for disaster response, national security, and environmental monitoring. This deal underlines the importance of dependable, repeatable commercial launch services for satellite constellation operators.
Investor angle: Rocket Lab’s expanding multi-launch agreements with international customers like Synspective demonstrate recurring revenue potential and international market traction. The company’s proven track record in deploying entire constellations efficiently strengthens confidence in Electron’s business model and positions Rocket Lab to capture more high-frequency SAR and constellation launch demand.
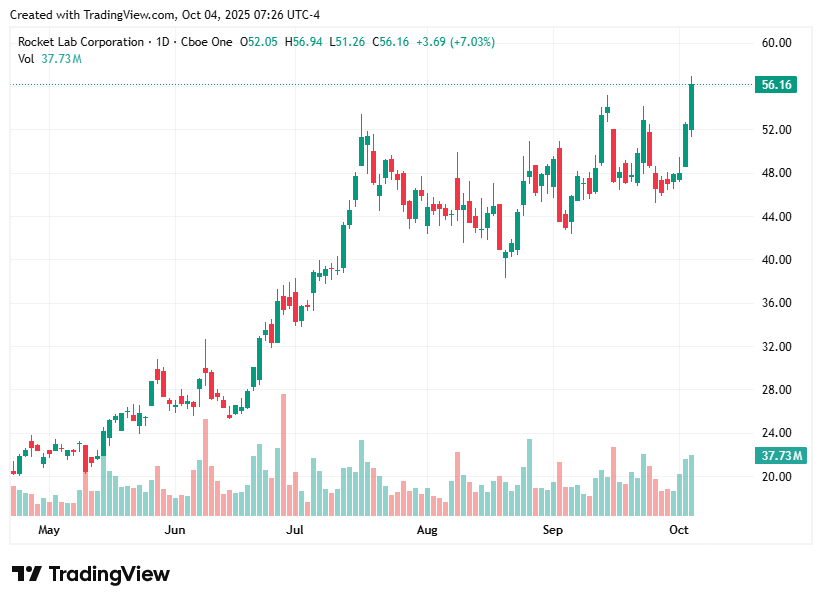
Read our latest analysis on RKLB
Rocket Lab 2Q25: Revenue and Margins Take Off
Rocket Lab just shared its Q2 2025 investor update on August 7, and it’s clear — the company is growing fast, not just in size but in what it can do. CEO Peter Beck and CFO Adam Spice walked investors through the numbers and milestones, and the message was loud and clear: Rocket Lab isn’t just launching rockets anymore — it’s building a full-stack space company with a serious role in national defense.
Arianespace and BULL Partner on Ariane 6 Space Debris Mitigation
What happened: In 2024, Arianespace and BULL signed a Memorandum of Understanding to pursue space debris mitigation for Ariane 6. A feasibility study found that installing BULL’s HORN PMD, a deployable sail that accelerates post-mission re-entry, on the Ariane 6 Dual Launch System would be effective. The partners aim for a flight demonstration of HORN on Ariane 6, with launch slots available from 2027. The effort aligns with Arianespace’s Net Zero Space commitments and French space-operations law (FSOA).
Why it matters: The collaboration underscores a growing emphasis on sustainable space operations and debris mitigation in the launch industry. By evaluating and pursuing a flight demonstration of HORN PMD on Ariane 6, Arianespace would help reduce debris risk and support Net Zero Space commitments and French law. If realized, the 2027 demonstration could position Ariane 6 as a leader in debris-mitigation technology.
Investor angle: The collaboration may strengthen Arianespace’s ESG profile and differentiate Ariane 6 by offering a debris-mitigation option. A successful demonstration could appeal to customers prioritizing sustainable operations and regulatory alignment. Risks include execution uncertainty, costs, and schedule for implementing HORN PMD and delivering the 2027 flight demonstration.
NASA and Australia Sign Bilateral Aeronautics and Space Cooperation Agreement
What happened: NASA announced the signing of a bilateral agreement with Australia to cooperate on aeronautics and space activities. The accord formalizes collaboration in aeronautics research and space operations between the United States and Australia. The agency notes that, due to a lapse in federal funding, NASA is not updating its website at this time.
Why it matters: This agreement highlights ongoing international collaboration in aerospace, aligning with industry trends toward multilateral research and technology exchange in aeronautics and space. It may enable joint research projects, shared facilities and standards, and coordinated efforts that could influence future programs and technology development despite current funding uncertainties.
Investor angle: The pact signals potential opportunities for US and Australian aerospace suppliers and technology developers as joint programs could expand cross-border contracts and collaboration. However, the impact remains contingent on future budget appropriations and program awards, meaning upside is tied to government funding and the realization of cooperative initiatives.
ESA and KASA Formalize Collaboration on Space Weather and Ground Station Use
What happened: On 1 October 2025, the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Korea AeroSpace Administration (KASA) announced a Memorandum of Understanding to cooperate on peaceful space activities, beginning with space weather monitoring and sharing space communications facilities. An implementing arrangement would allow mutual use of ground stations for telemetry, tracking and command, complementing an existing 2011 arrangement with KARI. The agreement also opens access to KASA’s Korea Deep Space Antenna in Yeoju and establishes a Joint Statement of Intent on space weather collaboration and capability development.
Why it matters: The pact strengthens Europe–South Korea space cooperation by expanding ground-network access and mission resilience through shared facilities, including ESA’s Estrack and Korea’s deep-space assets. It supports joint research on solar activity and space weather forecasting, with potential data collaboration between ESA’s Vigil mission to L5 and KASA’s planned solar probe to L4, contributing to a more comprehensive space weather service by the 2030s.
Investor angle: The agreement signals deeper international collaboration that could yield future joint missions and cost-sharing opportunities, particularly around navigation augmentation through the Korea Positioning System (KPS) and LEO-PNT collaborations. Although no immediate contracts are disclosed, broader access to ground infrastructure and enhanced mission reliability may create near- to mid-term potential for future procurement and program opportunities stemming from European–Korean space initiatives.
Solstar Wins NASA SBIR Contract to Develop Lunar Wi-Fi System
What happened: NASA awarded Solstar Space a Phase I Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) contract worth $150,000 to develop a Lunar Wi-Fi Access Point (LWIFI-AP) to support the Artemis program and Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS). Solstar will design a space-rated, multi-band wireless device capable of operating in extreme lunar conditions to enable real-time communications among astronauts, surface vehicles, and moon-orbiting assets, including potential use on landers, rovers, habitats, and the Lunar Gateway.
Why it matters: The contract targets NASA’s need for SWaP-efficient Wi-Fi and 3GPP communications across Artemis and CLPS assets. The LWIFI-AP is intended to provide a space-qualified, multi-mode, multi-protocol solution to support data flow, navigation, and scientific collaboration between crews, robotic systems, lunar vehicles, surface assets, and cislunar spacecraft, underpinning NASA’s goal of sustained lunar operations and broader cislunar connectivity.
Investor angle: The SBIR award validates Solstar’s approach to space-based connectivity and may pave the way for future NASA opportunities and commercial partnerships as Artemis and CLPS progress. The project lays groundwork for a flight-ready system that could be hosted on multiple lunar platforms, though success depends on achieving milestones through Phase I and any subsequent program steps.
Avio Secures €40M ESA Contract for Reusable Upper Stage Demonstrator
What happened: Avio signed a €40 million contract with the European Space Agency (ESA) on 29 September 2025 to develop reusable upper-stage technologies. The 24-month program aims to define the requirements, system design, and enabling technologies for a demonstrator capable of safely returning to Earth and being reused in future missions. Activities will cover both flight and ground segments, culminating in an integrated preliminary system design as part of Europe’s push toward full reusability.
Why it matters: The contract represents a significant step in Europe’s shift toward reusable launch capabilities, aligning with ESA’s vision to develop high-frequency launchers and an orbital logistics ecosystem. It builds on advances in liquid propulsion, re-entry, recoverability, and reusability, leveraging Avio’s LOX/methane propulsion expertise and Space Rider experience. The collaboration signals progress in Europe’s broader strategy to support reusable upper stages and potential evolutions of the Vega family and other systems.
Investor angle: The deal underscores Avio’s role in Europe’s reusable-launch ecosystem and could support longer-term growth in propulsion and systems integration. It signals strong collaboration with ESA and may pave the way for future contracts tied to higher launch cadence and lower costs. While the program targets a demonstrator with uncertain outcomes, the firm’s stated objective to enable higher launch frequency and competitive customer costs adds strategic value to Avio’s portfolio.
Beyond Gravity to Supply Robotic Arms for SWISSto12 GEO Satellites
What happened: Beyond Gravity secured a major contract to design and manufacture electric propulsion pointing mechanisms for five SWISSto12 HummingSat small geostationary satellites. The mechanism is a multi-axis robotic arm that will control the satellites’ electric thrusters to maintain precise track at 35,786 kilometers above Earth. Development and production are being led by Beyond Gravity, the Zurich, Switzerland-based space supplier, for SWISSto12’s new HummingSat fleet.
Why it matters: The contract demonstrates Beyond Gravity’s ability to deliver modular, flexible and scalable thruster pointing solutions in the form of a robotic arm for small GEO satellites. The company emphasizes that the solution offers high flexibility, modularity and series-production readiness, which it views as a potential new industry standard. This aligns with the growing need for precise propulsion pointing in small GEO constellations and highlights Beyond Gravity’s role in SWISSto12’s HummingSat program.
Investor angle: The five-satellite contract represents a major near-term revenue opportunity and reinforces Beyond Gravity’s positioning in electric propulsion pointing mechanisms. The emphasis on modularity and scalable production could support future orders if similar platforms are adopted in the market, though realized benefits will depend on execution and ongoing demand for such pointing systems.
We’d love your feedback on SpaceTech Weekly - help us improve and get 15% off our services!
Disclaimer: This article is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute investment advice. While we strive to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information presented, we cannot guarantee its completeness or correctness. Readers should conduct their own research and consult a qualified financial professional before making any investment decisions. Past performance is not indicative of future results.


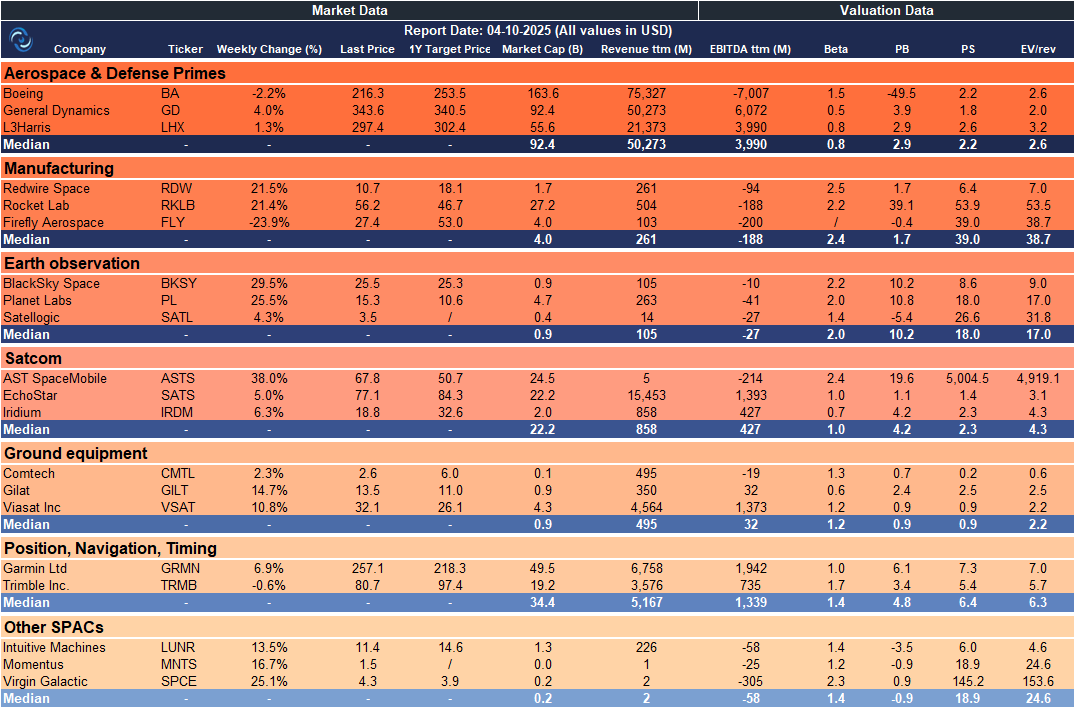
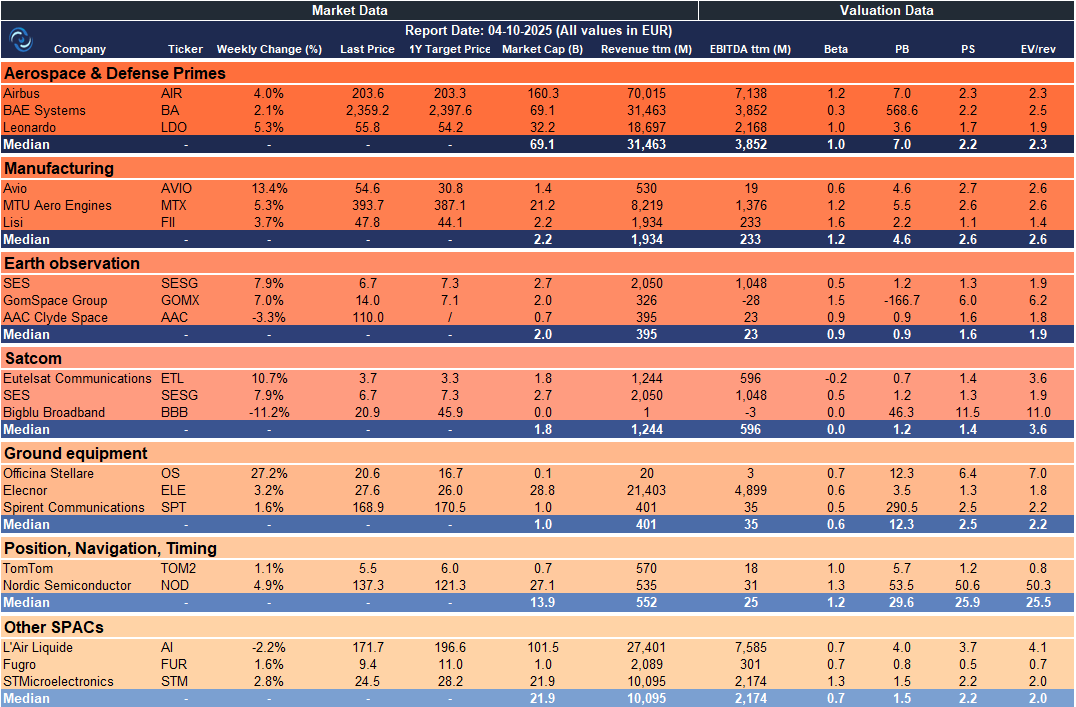


Excellent visualization by charts, Rocket Lab’s shows the market’s growing confidence in launch infrastructure.