SpaceTech Weekly Recap – September 22 - 28, 2025
Major funding, new missions, and setbacks: what mattered last week in space innovation.
Each week we bring you a curated look at the biggest moves in SpaceTech – from funding and M&A to market trends, contracts, and a quick stock snapshot.
“This week in SpaceTech, the sector showed strong momentum across funding, deals, and partnerships. Big money continues to flow into advanced manufacturing and AI-driven platforms, with Divergent Technologies raising $290M and Auterion securing $130M - clear signs of rising interest in dual-use tech and autonomous systems. On the launch side, activity remains high: Amazon is pushing ahead with Kuiper, while Europe’s Isar Aerospace and ArianeGroup landed important contracts that strengthen both commercial and sovereign access to space. At the same time, government support is accelerating, from Germany’s €35B defense investment to NASA’s growing private partnerships - underscoring how public and private players are working together to build the sector’s long-term infrastructure.” - Commentary by Matej Pretković
We provide consulting, fundraising support, market research, and advisory to help you grow and succeed. Contact us at mpretkovic@cyclopcorp.com.
Here is a quick overview of news:
M&A & Funding
Divergent Technologies Raises $290M to Scale AI-Driven Manufacturing
Quantum Space Acquires Phase Four Propulsion Assets to Strengthen In-Space Mobility
Auterion Secures $130M Series B to Expand AI Software for Drone Swarms
Firefly Aerospace Posts Strong Q2 After IPO
Near Space Labs Raises $20M to Grow Nationwide Stratospheric Imaging Platform
Market
Germany Plans €35B Investment to Boost Space Defense Capabilities by 2030
SES and HD PLUS Deepen German Collaboration on Hybrid SAT/IPTV Services
Launch
Avio Signs Launch Deal for Extra-European Satellite Customer
Isar Aerospace to Launch R-Space’s First GreenBox Satellites in 2026
Atlas V Launches Kuiper-3 Satellites, Advancing Amazon’s Broadband Constellation
Contracts
ArianeGroup and MT Aerospace Sign Key Ariane 6 Supplier Contract
Zeno Power Secures Americium-241 Supply for Lunar Nuclear Batteries
NASA Taps Private Company to Extend Swift Spacecraft Operations
Planet Labs Expands Satellite Manufacturing in Germany
Space Forge and United Semiconductors Partner on Space-Based Chip Manufacturing
Read our latest weeklies for more recent SpaceTech updates
Stay up to date with funding, deals, trends, contracts, and market insights in one weekly update.
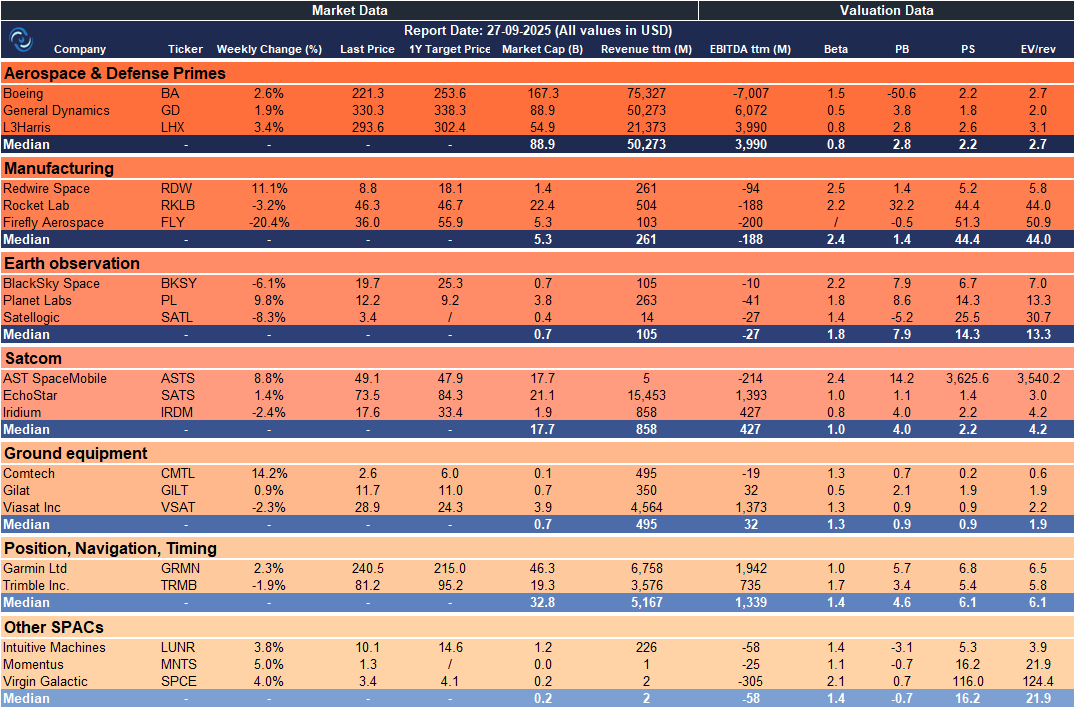
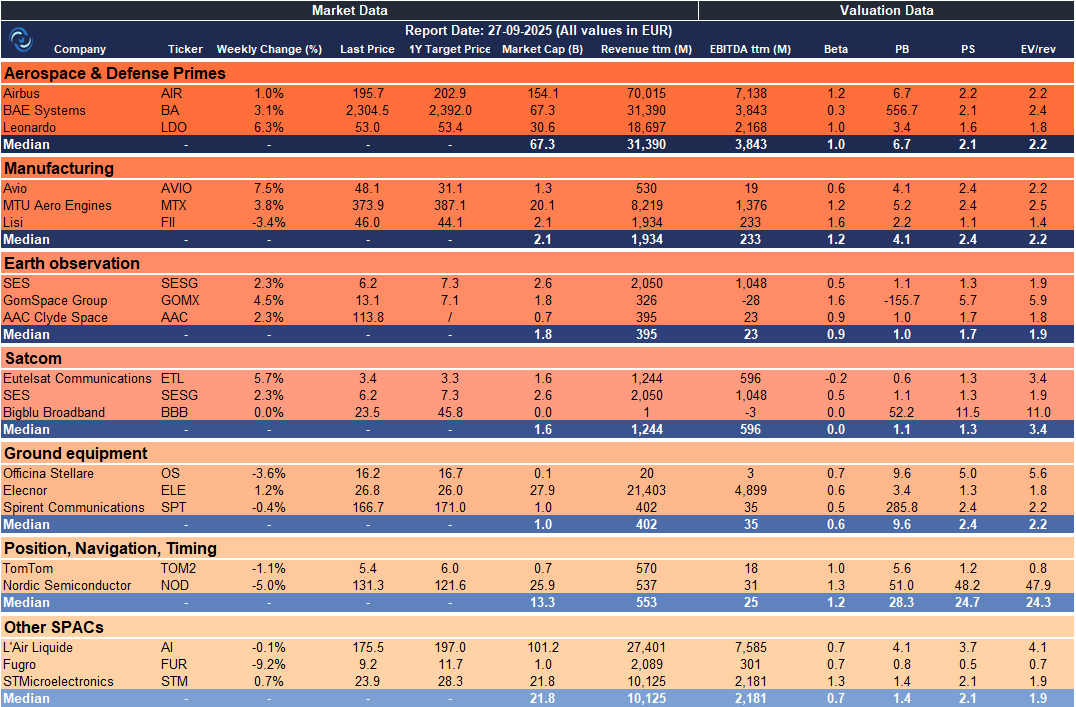
Weekly SpaceCap - These tables track weekly stock performance and key metrics for global and European SpaceTech companies, giving a quick snapshot of market trends.
US – SpaceTech Stocks Snapshot
Europe – SpaceTech Stocks Snapshot
Need a full breakdown by sector or a customized template with your own metrics? Get in touch with us at mpretkovic@cyclopcorp.com.
Read the news in more detail:
M&A & Funding
Divergent Technologies Raises $290M to Scale AI-Driven Manufacturing
What happened: Divergent Technologies has closed a $290 million Series E round, led by Hexagon AB, to expand its digital manufacturing platform that integrates AI-driven design, additive manufacturing, and automated assembly. The funding will accelerate production capacity as the company takes on growing U.S. defense contracts, positioning it as a key supplier in both automotive and national security sectors.
Why it matters: It underscores how advanced, flexible manufacturing is becoming central to U.S. defense re-industrialization. Divergent’s model reduces lead times and costs while strengthening supply chain resilience—capabilities the Pentagon increasingly prioritizes. The raise reflects broader industrial policy momentum toward reshoring and scaling critical production.
Investor angle: The deal highlights strong appetite for dual-use advanced manufacturing companies. Strategic backing from Hexagon AB provides both capital and ecosystem integration, while the round’s size signals confidence in Divergent’s trajectory toward IPO or acquisition. The company stands out as a scalable platform at the intersection of defense demand and industrial digitization.
Quantum Space Acquires Phase Four Propulsion Assets to Strengthen In-Space Mobility
What happened: Quantum Space has acquired Phase Four’s Maxwell Block 2 and Block 3 electric propulsion assets, integrating the technology and IP into its platform for cislunar and deep-space mobility. The move enhances Quantum’s ability to deliver end-to-end in-space transportation and infrastructure support.
Why it matters: This matters as propulsion is a core enabler of the expanding space economy, particularly for missions beyond low-Earth orbit. By adding Phase Four’s flexible thrusters, Quantum strengthens its offering for government and commercial customers seeking scalable and resilient mobility solutions.
Investor angle: Strategically, the deal creates a moat by integrating Phase Four’s multi-mode propulsion with Quantum Space’s Ranger platform, potentially expanding addressable revenue across national security, civil science, and commercial customers from LEO to GEO and cislunar space. The deal signals consolidation in the sector and increases Quantum’s long-term value ahead of future contracts and capital raises.
Auterion Secures $130M Series B to Expand AI Software for Drone Swarms
What happened: Auterion announced a $130 million Series B led by Bessemer Venture Partners to scale its AI-enabled AuterionOS platform and the Nemyx defense system, with a strategy to turn commercial low-cost drones into coordinated swarms across air, land, and sea.
Why it matters: Signals a shift toward battlefield software that combines AI with mass-produced, affordable hardware to enable drone swarms at scale. The round includes $25 million non-dilutive funding from the US Department of War, underscoring government interest and geopolitical implications. If successful, it could reshape defense procurement, competitive dynamics among drone/software providers, and rapid deployment of autonomous capabilities.
Investor angle: Led by Bessemer Venture Partners, with Lakestar, Mosaic Ventures, and Costanoa Ventures participating; the government-backed component may de-risk scaling but adds strategic exposure. Opportunities for defense-prime partnerships and exits through software ecosystems exist, alongside regulatory and ethical considerations around dual-use AI and autonomous weapons deployment.
Firefly Aerospace Posts Strong Q2 After IPO
What happened: Firefly Aerospace released its second-quarter 2025 results following its recent IPO. The company reported a strong balance sheet, increased its backlog to about $1.3 billion by end of July, and achieved FAA clearance for its Alpha rocket to return to flight. They also disclosed NASA awarded a $10 million contract addendum and that they have raised net proceeds of $933.1 million from the IPO.
Why it matters: As Firefly begins life as a public company, the results show both opportunities and challenges. The growing backlog validates demand for its space and lunar mission services, while the FAA clearance is critical for restoring investor confidence after launch setbacks. These developments support Firefly’s positioning in the increasingly competitive commercial launch and lunar services markets.
Investor angle: For investors, this report provides a first real test of Firefly’s post-IPO trajectory. The robust backlog and cash from the IPO offer a cushion, but execution risk remains—especially in launch reliability and managing growth. The NASA addendum and regulatory clearance are positive signals, but future upside will depend on meeting mission milestones, maintaining capital discipline, and delivering dependable launch performance.
Moon Mission Maker Firefly Aerospace Launches IPO on the Nasdaq
Firefly Aerospace has launched its IPO today, trading under the ticker symbol FLY on the Nasdaq exchange.
Near Space Labs Raises $20M to Grow Nationwide Stratospheric Imaging Platform
What happened: Near Space Labs announced a 20 million Series B to scale its stratospheric imaging platform. Bold Capital Partners led the round with participation from USAA, Climate Capital, Gaingels, River Park Ventures, and existing investors Crosslink Capital, Third Sphere, and Draper Associates. The funds will accelerate expansion of the Swift robot fleet to provide nationwide, high-resolution imagery across the continental United States, targeting about 80 percent of the population twice per year at 7 cm resolution to support AI-enabled workflows in industries such as property and casualty insurance.
Why it matters: The investment validates demand for frequent, high-resolution geospatial data beyond satellites or traditional drone surveys. The stratospheric approach offers satellite-like coverage with faster delivery and lower costs, enabling improved underwriting, risk assessment, and claims processing for insurance, and potential broad adoption across other sectors relying on geospatial intelligence.
Investor angle: Key upside for investors includes a differentiated, scalable data platform with a large addressable market in insurance and risk management, a fleet-based model capable of rapid nationwide coverage, and strategic backing from insurers (USAA) and tech-forward funds (Bold Capital). The round signals strong confidence in Near Space Labs’ ability to monetize geospatial data at scale as AI-driven workflows expand.
Market
Germany Plans €35B Investment to Boost Space Defense Capabilities by 2030
What happened: Germany’s Defense Minister Boris Pistorius announced on September 25, 2025, that the Bundeswehr will invest €35 billion by 2030 to strengthen its space security infrastructure. The investment will cover hardened satellite systems, radars, telescopes, “guardian satellites,” redundant constellations, secure launch capabilities, and a dedicated military satellite operations center. The move aims to ensure Germany can defend its space assets and maintain operational freedom in orbit, particularly in light of growing capabilities from Russia and China.
Why it matters: The plan underscores the increasing strategic importance of space as a domain for both civilian and military operations. Satellites now underpin communication, navigation, weather, and logistics, making them critical infrastructure. Germany’s investment reflects a broader European trend of preparing for hybrid threats and potential attacks in space, emphasizing resilience, innovation, and international cooperation.
Investor angle: The initiative opens opportunities for European aerospace and defense companies, particularly dual-use satellite manufacturers, launch service providers, and space-tech innovators. Early engagement with small and medium enterprises and start-ups is encouraged, highlighting a shift toward public-private collaboration in securing critical space infrastructure. This €35 billion commitment signals strong government demand and long-term market potential in space technologies across Europe.
SES and HD PLUS Deepen German Collaboration on Hybrid SAT/IPTV Services
What happened: SES and HD PLUS GmbH announced closer cooperation in Germany following a leadership change at HD PLUS GmbH. Christoph Mühleib, currently Managing Director at SES in Germany, will take over from Andreas Müller-Vondey as the new Managing Director of HD PLUS, signaling a move to align SES’s satellite operations with HD Plus’s hybrid SAT/IPTV platform.
Why it matters: The move signals deeper strategic alignment in the German market, potentially enabling joint go-to-market, content distribution, and technology integration that could strengthen the market position for both parties and accelerate development of hybrid satellite/IPTV services.
Investor angle: The development could imply potential synergies and revenue growth in Germany, a key market for HD Plus; monitor for formal milestones, integration plans, and any execution risks tied to leadership transition and operational integration.
Launch
Avio Signs Launch Deal for Extra-European Satellite Customer
What happened: Avio USA and Raytheon (RTX) expanded their collaboration on the Mk 104 dual-thrust solid rocket motor by executing a purchase order for up to $26 million to fund continued engineering through the Critical Design Review, procurement of long-lead materials for qualification, and to bolster production capacity for Raytheon’s Standard Missile franchise. This follows prior System Requirements Review and Preliminary Design Review and aims to accelerate qualification and production readiness.
Why it matters: The deal strengthens the defense propulsion supply chain for critical missiles, enhances resilience and capacity through second-sourcing of key materials, and supports readiness for Raytheon and allied customers. It indicates sustained collaboration between Avio and Raytheon and could pave the way for full-scale production and additional contracts tied to national security programs.
Investor angle: The arrangement provides visibility into a multi-year defense propulsion program with potential revenue from engineering funding and future production. Risks include milestones timing, potential cost overruns, dependence on defense budgets and regulatory approvals, exposure to long-lead material sourcing, and geopolitical factors that could impact contract awards.
Isar Aerospace to Launch R-Space’s First GreenBox Satellites in 2026
What happened: Isar Aerospace and R-Space signed a launch service agreement under the ESA Marketplace ScaleUp program to launch two R-Space satellites aboard Isar’s Spectrum launch vehicle in 2026 from Andøya Spaceport, with additional flights planned for 2026 and 2027. The satellites will conduct in-orbit demonstrations to validate next-generation satellite technologies.
Why it matters: The deal strengthens European collaboration and advances the ESA Marketplace’s goal of accelerating deployment of new space technologies. It supports faster time-to-orbit through in-orbit demonstration services, expands Europe’s small-to-medium satellite launch and tech-validation ecosystem, and provides Isar Aerospace and R-Space with a multi-flight pipeline.
Investor angle: Near-term catalyst: first launch in 2026 under a European public–private program; potential revenue from multiple flights (2026–27) and the IOD/IOV services business. Long-term implications include scaling European launch capacity, diversification of Isar’s and R-Space’s offerings, and potential competitive advantages in a growing market; risks include program delays, execution risk, and competition from other launch providers.
Atlas V Launches Kuiper-3 Satellites, Advancing Amazon’s Broadband Constellation
What happened: ULA’s Atlas V 551 launched from Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral on Sept. 25 at 8:09:30 a.m. EDT, delivering a batch of Project Kuiper satellites to orbit for Amazon on the Kuiper 3 mission. The rocket configuration included five side-mounted solid rocket boosters and a 5.4-meter medium payload fairing; the Centaur upper stage uses an RL10C-1-1 engine. The mission is part of Amazon’s plan to deploy a global constellation of more than 3,200 LEO satellites under the largest commercial launch agreement to date, using Atlas V and Vulcan rockets.
Why it matters: This milestone advances Amazon’s Project Kuiper, a major global broadband initiative. It demonstrates the capability of the commercial launch sector to scale large satellite constellations, reinforces ULA’s role in delivering high-profile commercial missions, and could drive sustained launch demand and revenue for the industry as the Kuiper program progresses toward full deployment.
Investor angle: Key investment implications include potential revenue visibility for ULA from the Amazon contract (reported as a large, ongoing arrangement involving multiple Atlas V and Vulcan launches) and the broader growth of the commercial satellite broadband market. Benefits depend on cadence and cost control of future launches; risks include schedule slippage, regulatory or technical hurdles, competition from other constellations, and capex needs to support a high-volume launch pipeline.
Contracts
Zeno Power Secures Americium-241 Supply for Lunar Nuclear Batteries
What happened: Zeno Power signed a strategic deal with Orano to secure multi-year supplies of americium-241 (Am-241) from La Hague’s fuel recycling operations. Zeno will invest several million dollars for priority access, supporting its americium-fueled space nuclear batteries for NASA’s lunar rovers, landers, and infrastructure, complementing its existing Sr-90 supply and reducing reliance on scarce Pu-238.
Why it matters: Provides a stable, diversified Am-241 supply for space power systems, reducing reliance on limited Pu-238 and advancing Artemis-era missions. Demonstrates the value of recycling used nuclear fuel and strengthens Zeno’s multi-fuel platform (americium for space, strontium for maritime/terrestrial) with cross-industry applications and DoD/NASA potential.
Investor angle: The move offers long-term strategic revenue from Am-241 contracts while requiring near-term capex. Key risks include regulatory approvals, export controls, and reliance on government customers, but the deal builds a moat against Pu-238 shortages and creates upside from expanded production and new contracts.
ArianeGroup and MT Aerospace Sign Key Ariane 6 Supplier Contract
What happened: ArianeGroup has renewed its partnership with Germany’s MT Aerospace AG to supply tanks and major structural components for the upper and core stages of Ariane 6, covering flight models 16 to 42. The agreement supports the industrial ramp-up of Europe’s heavy-lift launcher and continues a longstanding collaboration that has been critical across previous Ariane programs.
Why it matters: The contract reinforces Europe’s independent access to space and ensures continuity in the production of Ariane 6, which is central to European space sovereignty. It highlights the strategic role of industrial partnerships in maintaining competitiveness and operational reliability in the launch sector.
Investor angle: The deal signals long-term revenue visibility for MT Aerospace and emphasizes Germany’s industrial contribution to Europe’s space infrastructure. For investors, it underscores the stability and growth potential within the European launch supply chain, particularly for companies supporting heavy-lift launch capabilities.
NASA Taps Private Company to Extend Swift Spacecraft Operations
What happened: NASA awarded a contract to a private company to attempt an orbital boost for the Swift spacecraft, with the goal of extending its operational life or repositioning it for future observations.
Why it matters: A successful maneuver could extend Swift’s science operations, enabling continued study of gamma-ray bursts and high-energy events. It also highlights NASA’s approach of using industry partnerships to prolong asset lifetimes, potentially saving costs and showcasing commercial capabilities in spacecraft servicing.
Investor angle: For investors, this signals opportunities in space services and public‑private partnerships. Successful servicing could lead to follow‑on contracts and revenue for the provider, while risks—such as technical challenges or funding shifts—could affect timelines and returns. Monitor NASA procurement cycles and budget expectations for mission extension programs.
Planet Labs Expands Satellite Manufacturing in Germany
What happened: Planet Labs Germany, the German subsidiary of the US space firm Planet Labs, announced a major expansion to manufacture its Pelican high-resolution Earth observation satellites in Berlin, with an investment described as a significant eight figures and an aim to double production capacity.
Why it matters: The move strengthens Europe’s domestic satellite manufacturing capability, expands Germany’s role in Europe’s space infrastructure, and reinforces public-private collaboration with the German government; it could accelerate access to timely Earth imagery for security, governance and commercial use while shaping regional competition and supply chains.
Investor angle: The Berlin production expansion is backed by a significant eight-figure investment and comes alongside a €240 million government collaboration, potentially driving revenue growth from European customers and expanding Planet Labs’ footprint in Europe; risks include regulatory changes, export controls and competitive pressure from other satellite manufacturers.
Space Forge and United Semiconductors Partner on Space-Based Chip Manufacturing
What happened: Space Forge and United Semiconductors signed an MoU to collaborate on space-based semiconductor manufacturing. The partnership will combine Space Forge’s microgravity-enabled deposition with United Semiconductors’ crystal growth and wafer expertise to develop advanced processes, space-compatible equipment for the ForgeStar platform, and identify materials suited for in-orbit production. The MoU sets a framework for moving quickly toward commercial projects in quantum computing, power electronics, sensors, and displays.
Why it matters: The deal advances U.S.-led onshore semiconductor supply chains by pairing terrestrial and in-space capabilities to meet demand for ultra-high quality substrates. It reflects growing momentum in space manufacturing and supports the future LEO economy while bolstering domestic leadership in critical technologies.
Investor angle: The collaboration offers exposure to a high-growth space-enabled semiconductor market with long-term upside in quantum and advanced electronics. Key milestones include validating deposition processes, building flight-ready equipment, and securing market pathways. Risks lie in technical timelines, regulation, and adoption, but successful execution could open attractive investment opportunities in both partners and the broader sector.
We’d love your feedback on SpaceTech Weekly - help us improve and get 15% off our services!
Disclaimer: This article is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute investment advice. While we strive to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information presented, we cannot guarantee its completeness or correctness. Readers should conduct their own research and consult a qualified financial professional before making any investment decisions. Past performance is not indicative of future results.